The complete guide to OpenTelemetry in Next.js
Published February 10, 2025
OpenTelemetry is an important specification that defines how we send telemetry data to observability backends like LaunchDarkly, Grafana, and others. OpenTelemetry is great because it is vendor agnostic, and can be used with several observability backends. If you’re new to OpenTelemetry, you can learn more about it here.
This complete guide to OpenTelemetry in Next.js covers high-level concepts as well as how to send traces, logs, and metrics to your OpenTelemetry backend of choice.
Setting Up OpenTelemetry for Next.js: Tracing, Logging, and Metrics
Let’s walk through setting up OpenTelemetry in a Next.js project, covering:
- Tracing: Capturing distributed traces for API requests and page transitions
- Logging: Collecting structured logs that correlate with traces
- Metrics: Exporting performance and custom application metrics
There are several reasons that make OTel a great choice for monitoring your Next.js application:
- Built-in Spans: Next.js provides automatic spans at the framework level
- Exception Tracking: Errors are automatically captured within traces by the framework
- Simplified Setup: @vercel/otel eliminates the need to manually configure OpenTelemetry SDKs, exporters, and instrumentations
By the end of this tutorial, you’ll have all the observability data you need to be proactively notified when something goes wrong, troubleshoot issues quickly, and fix performance bottlenecks in the critical parts of your code.
Installing OpenTelemetry in Next.js
We’ve covered instrumenting Next.js with @vercel/otel in our blog post on using @vercel/otel in Next.js.
While @vercel/otel is a simpler option for many applications, it may not give you full control over the OpenTelemetry SDKs.
Today, we’ll go through a complete guide to setting up OpenTelemetry from scratch, explaining the configuration options along the way.
To get started, install the necessary OpenTelemetry dependencies:
This setup includes the core OpenTelemetry API, SDK, HTTP and Fetch instrumentations, and OTLP exporters for traces and metrics.
Setting Up the OpenTelemetry SDK
Create a new file otel.ts at the root of your Next.js project:
To trigger this file to run when the app starts, you can invoke it from the Next.js magic instrumentation.ts file.
The instrumentation.ts file is automatically detected by Next.js and will run when the app starts. Before Next.js 15, the instrumentation is experimental, so you will have to enable it explicitly:
Configuring Tracing
With the SDK configured, your application will start to export the telemetry data using the exporters defined. However, you may wonder what data is being captured without any explicit code added.
Next.js has built-in OpenTelemetry spans for various parts of the application, including:
- API routes (
pages/apiorapp/api) - Page router (Pages Directory)
- App router (App Directory)
Some top-level spans are emitted out-of-the-box, while others can be turned on by turning on verbose logging:
Setting the NEXT_OTEL_VERBOSE environment variable will emit additional traces that give you more granularity of the code execution.
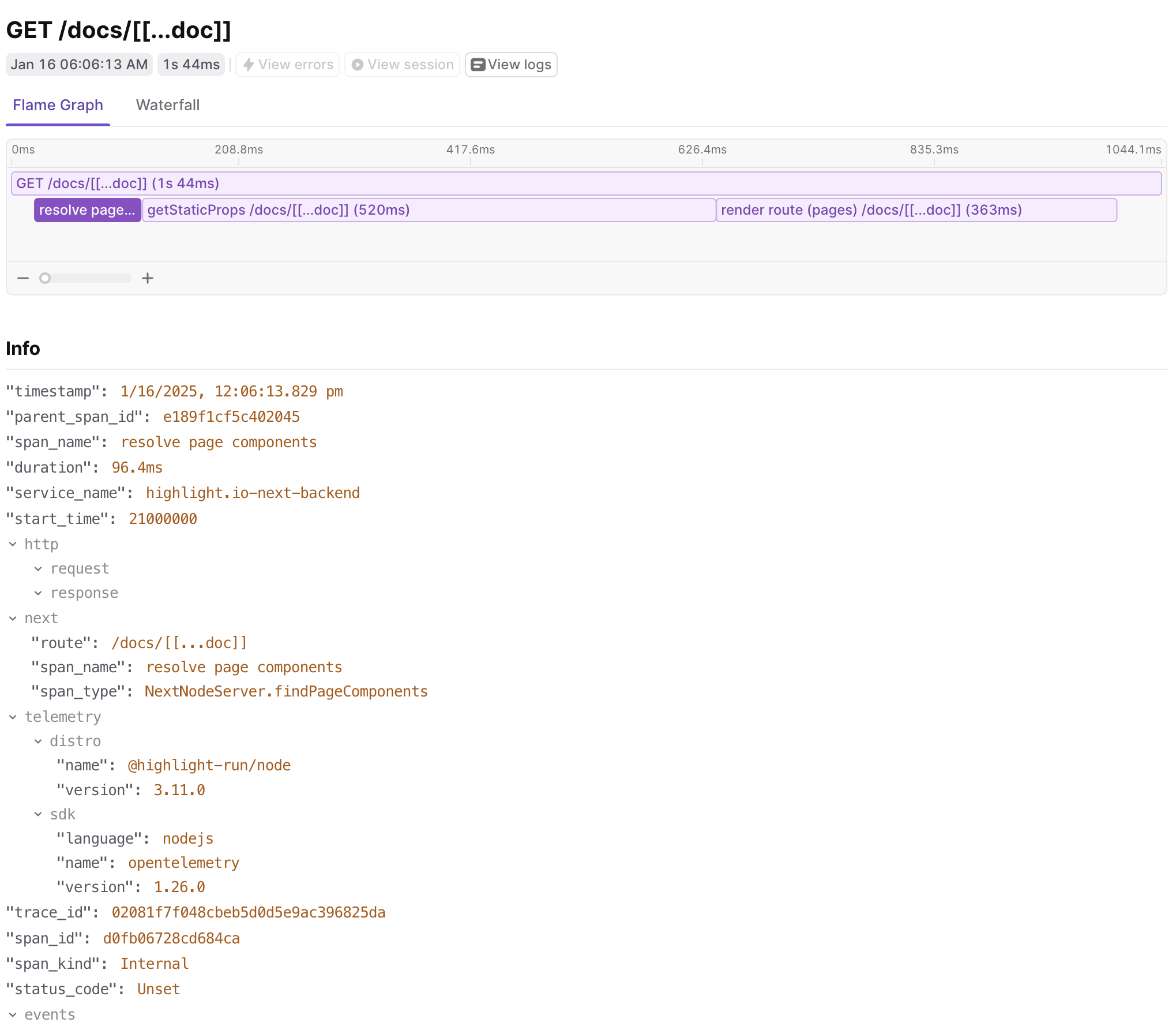
For example, here’s a flame graph visualization of a trace without verbose tracing, NEXT_OTEL_VERBOSE=0:
And here’s the same trace with verbose tracing enabled, NEXT_OTEL_VERBOSE=1:
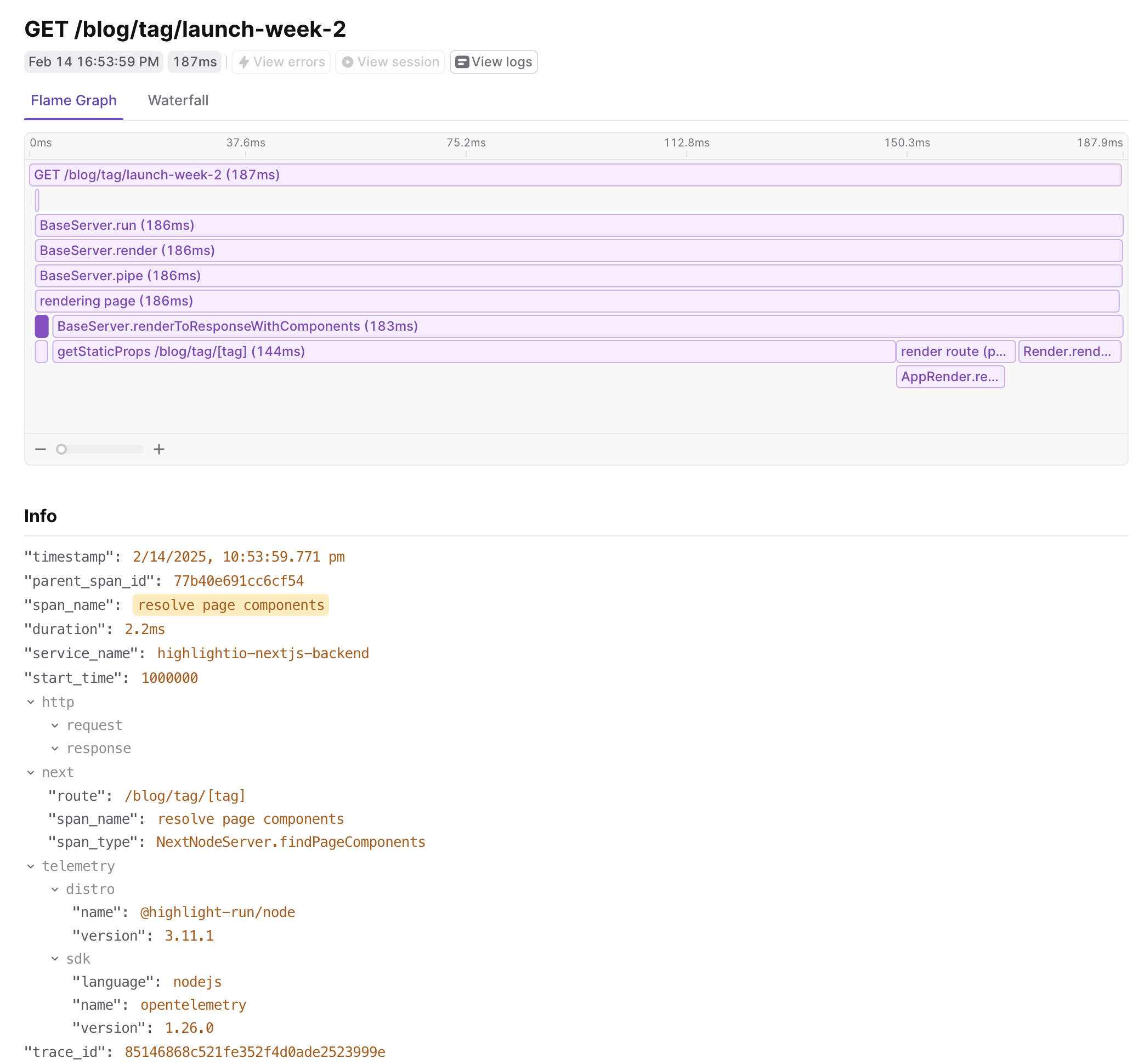
Let’s go through some examples of the data that can be captured.
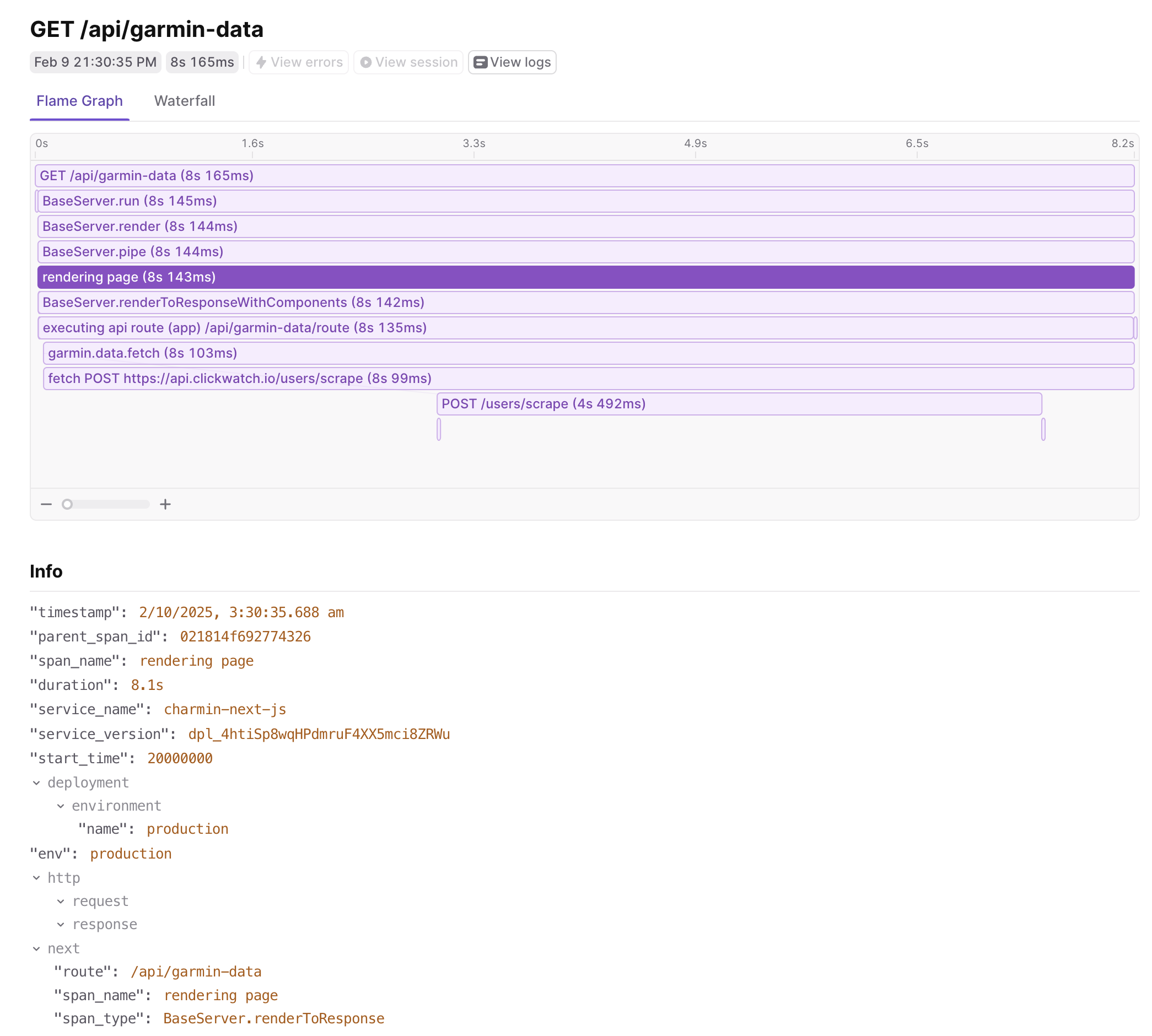
In the image above, you can see the trace start with an api route request that is piped through Next.js to the API handler.
We also see a custom span that wraps an outgoing API request to another service. Because we set up auto-instrumentation,
we capture the fetch call automatically, and can even propagate the trace context to the backend service.
Here’s a list of the top-level spans that are captured automatically by Next.js:
- BaseServer.handleRequest - Named
[http.method] [next.route], the root span for each incoming request to your Next.js application. - AppRender.getBodyResult - Named
render route (app) [next.route], represents the process of rendering a route in the app router. - AppRender.fetch - Named
fetch [http.method] [http.url], represents the fetch request executed in your code. - AppRouteRouteHandlers.runHandler - Named
executing api route (app) [next.route], represents the execution of an API Route Handler in the app router. - Render.getServerSideProps - Named
getServerSideProps [next.route], represents the execution of getServerSideProps for a specific route. - Render.getStaticProps - Named
getStaticProps [next.route], represents the execution of getStaticProps for a specific route. - Render.renderDocument - Named
render route (pages) [next.route], represents the process of rendering the document for a specific route. - ResolveMetadata.generateMetadata - Named
generateMetadata [next.page], represents the process of generating metadata for a specific route. - NextNodeServer.findPageComponents - Named
resolve page components, represents the process of resolving page components for a specific page. - NextNodeServer.getLayoutOrPageModule - Named
resolve segment modules, represents loading of code modules for a layout or a page. - NextNodeServer.startResponse - Named
start response, represents the process of starting the response for a specific route.
See the Next.js docs for more details.
Whether you have an API route, a page route, or an app route, you’ll see a span for each request. Spans will carry details such as what route was requested, how long each step of the processing took, and what metadata was provided in the HTTP request.
The power lies in connecting the automatic spans with custom ones and ones provided by additional OpenTelemetry instrumentations. As shown in the image above, when the app route api method makes an outgoing HTTP request to another service (in this case, an example Python service), the trace will capture the duration of the backend API request and the response status code. At a glance, that can help diagnose a performance issue due to a downstream service or a failed backend API call.
Logging in OpenTelemetry
Let’s add some more logic to otel.ts to create a logger that can be used to emit custom messages.
You can use this logger in your code or with a helper method. Make sure to check out other OpenTelemetry logging instrumentations that can automatically hook into common logging libraries like Winston or Pino.
If you want to capture console logger methods such as console.log, console.error, etc.,
you’ll need to manually instrument them to record their logs to the OpenTelemetry logger.
Here’s an example of how to do that:
Capturing Exceptions with Spans
Let’s emit a custom span in our code that can be used to capture an exception. We’ll start a span and then automatically add error attributes by capturing the error. Modify your API route:
This ensures that the error is captured within the OpenTelemetry trace and can be visualized in your tracing backend.
Next.js 15 also introduces a new onRequestError hook that can be used to capture server errors.
You can use it in your instrumentation.ts file to intercept all server actions and capture the error:
This example reports the error to the current active span, which is the span for the request.
Exporting Metrics
Next.js applications often benefit from metrics like request count, latency, and errors. Here’s how to add instrumentation for request tracking in otel.ts:
Then, use it in an API route:
Putting it all together
Let’s put all of the pieces together and create a complete otel.ts file that will automatically instrument your Next.js app. Using @vercel/otel, we’ll configure export for LaunchDarkly, but you can use any other OpenTelemetry-compatible backend:
Now, let’s use the OpenTelemetry SDK in our route to emit data:
In this full handler example, you can see how to emit a trace, log, and metric using the native OpenTelemetry constructs. It’s evident that the API is quite verbose and not simple to work with. For the LaunchDarkly platform, we’ve created a Node.js SDK that wraps OpenTelemetry to simplify the API streamline data reporting, with simple APIs. For example, here’s the same handler using our SDK:
Conclusion
With the full suite of instrumentation configured, you’ll start to see valuable data in your LaunchDarkly dashboard. This data empowers you to enhance your troubleshooting workflows significantly.
By visualizing response times, error rates, and detailed error reports, you can quickly identify performance bottlenecks and areas for improvement. For instance, if you notice a spike in response times for a specific API endpoint, you can drill down into the traces to see what might be causing the delay.
Additionally, the error rate metrics allow you to monitor the health of your application in real-time. If an increase in errors is detected, you can leverage the detailed error reports to understand the context and root cause, enabling you to address issues proactively.
Overall, integrating OpenTelemetry with LaunchDarkly not only provides you with observability but also equips you with the insights needed to optimize your application and enhance user experience. Start leveraging this powerful combination today to take your monitoring and troubleshooting capabilities to the next level!
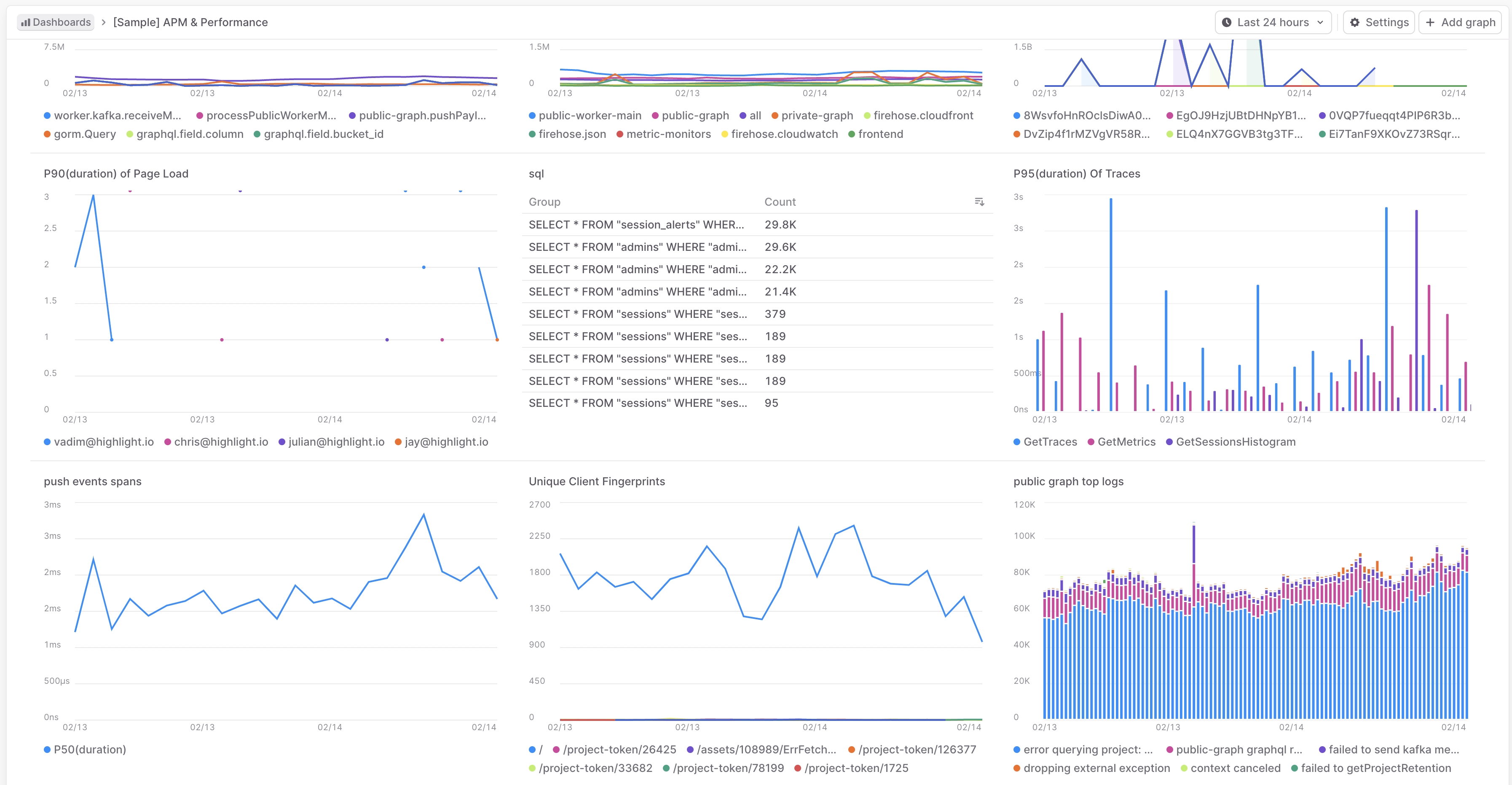
You can see the traces, logs, and metrics in the dashboard and use them to troubleshoot issues and optimize your application.
